Transgender
The Damage Caused by Trans ‘Inclusion’ In Female Athletics: a Massachusetts Case Study
A single biologically male high-school student has invaded female categories in at least four different sports—negatively affecting hundreds of girls and women in the process.
· 18 min read
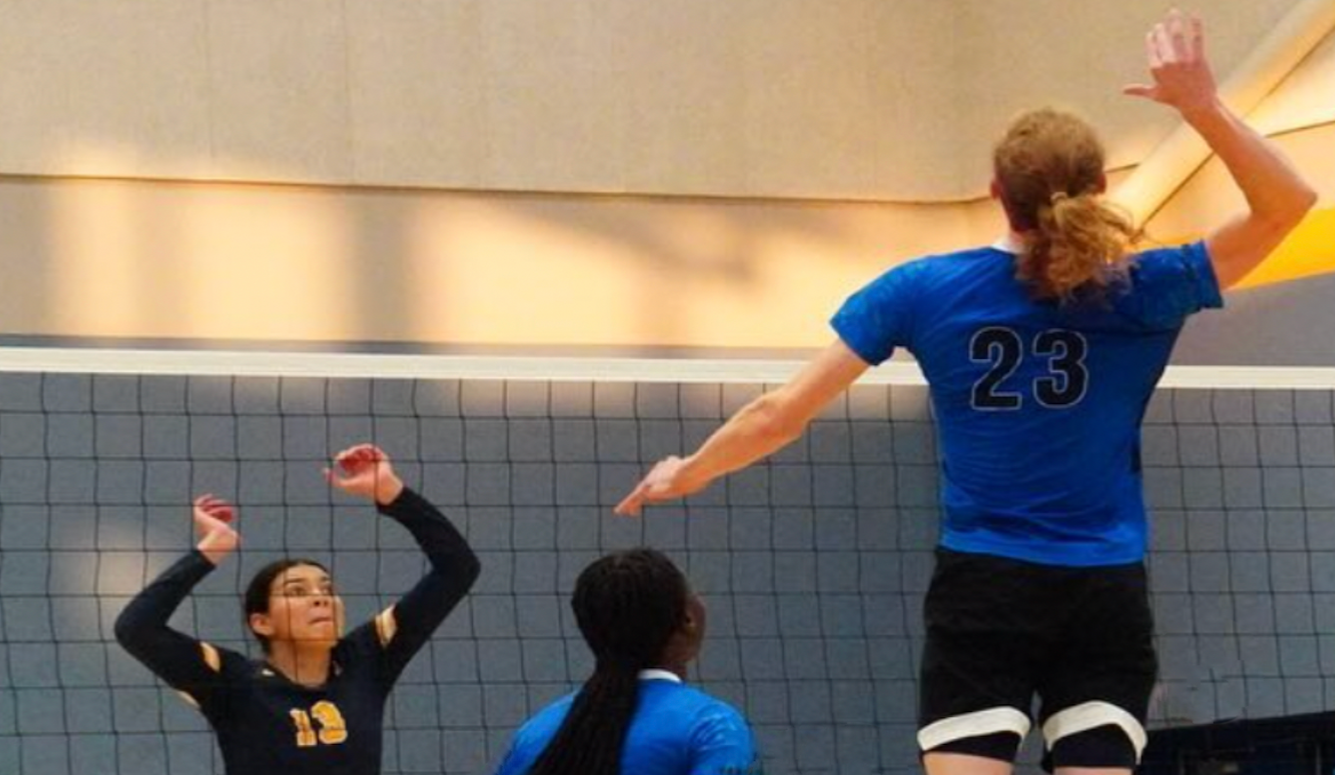

“A 6’ Tall, Bearded Trans Basketballer Arrogantly Slams a Young Girl to the Ground—She Collapses in Agony,” was how Britain’s Daily Mail headlined the latest transgender sports scandal. Some may roll their eyes at the Mail’s sensationalist (and uniquely verbose) headline style. But in this case, at least, no one can accuse the newspaper’s copy editors of getting the facts wrong.
Keep reading
Natalism and the Welfare Mother
Stephen Eide
· 6 min read
A New Middle East?
Brian Stewart
· 6 min read
Greta Thunberg’s Fifteen Minutes
Allan Stratton
· 10 min read
Gentrifying the Intifada
John Aziz
· 8 min read
Creative Writing in the Age of Trump
Daphne Merkin
· 7 min read