Environment
The End of the World as We Know It?
The scholars at Our World in Data add that this also holds for other natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcano activity, wildfire, and landslides.

How is the world going to end? Polls consistently show that most believe the cause will be environmental. “Climate anxiety” has reached such a fevered pitch among young people across the globe that the Lancet recently issued a special “call to action” to help with the problem. Clinicians have even created “climate anxiety scales” to measure the runaway angst spreading through our children, and the rest of us.
But what if the best, emerging science is actually telling us quite firmly that such fears are not only deeply misplaced, but that the most realistic cause of our collective human demise is likely the precise opposite of what most assume? This is the conclusion of a very interesting body of highly sophisticated and inter-disciplinary research. The greatest threat to humanity’s future is certainly not too many people consuming too many limited natural resources, but rather too few people giving birth to the new humans who will continue the creative work of making the world a better, more hospitable place through technological innovation. Data released this summer indicates the beginning of the end of humanity can be glimpsed from where we now stand. That end is a dramatic population bust that will nosedive toward an empty planet. New research places the beginning of that turn at about 30 years from today.
This means that Thomas Robert Malthus, and his many influential disciples, had it precisely wrong. More people are not only not the problem, but a growing population is the very answer to a more humane future in which more people are living better, healthier, longer lives than they ever have in our race’s tumultuously dynamic history.
We are not killing the planet
Pop voices like those of Congresswoman Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Swedish teenage activist Greta Thunberg and countless Hollywood celebrities have warned that unless drastic action is taken at once, we face irrevocable global catastrophe. The Climate Clock in Manhattan’s Union Square pegs the start of the Earth’s deadline at a little more than seven years from today. But this is not science. The most sophisticated examination considering the Earth’s eco-deadline was just published in August in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution. Drawing upon 36 meta-analyses, involving more than 4,600 individual studies spanning the last 45 years, nine ecologists, working from universities in Germany, France, Ireland, and Finland, explain that the empirical data simply does not permit the determination of any kind of environmental dooms date, or “thresholds” as scientists call them.
These scholars state frankly: “We lack systematic quantitative evidence as to whether empirical data allow definition of such thresholds” and “our results thus question the pervasive presence of threshold concepts” found in environmental politics and policy today. They explain that natural bio-systems are so dynamic—ever evolving and adapting over the long-term—that determining longevity timeframes is impossible. Talk of a ticking eco-clock is simply dogma. Two major books published in 2020 serve as carefully researched and copiously documented critiques of environmental scaremongering. Both are written by pedigreed progressive environmentalists concerned about the irrationally wild rhetoric of late.
The first is Apocalypse Never: Why Environmental Alarmism Hurts Us All by Michael Shellenberger, who TIME magazine has lauded as a “hero of the environment.” Shellenberger explains that not only is the world not going to end due to climate catastrophe, but in very important ways, the environment is getting markedly better and healthier. He adds that technology, commerce, and industry are doing more to fix the Earth’s problems than Greenpeace and other activists. As an environmentalist, he is strongly pro-people and pro-technology, explaining counter-intuitively that the scientific “evidence is overwhelming that our high-energy civilization is better for people and nature than the low-energy civilization that climate alarmists would return us to.” He is right.
The other major environmentalist challenging eco-doom is Bjørn Lomborg of the Copenhagen Consensus Center, a think tank that seeks global solutions to humanity’s most pressing problems. The Guardian feted Lomborg as “one of the 50 people who could save the planet.” In his book False Alarm, he explains how “climate change panic” is not only unfounded, but wasting trillions of dollars globally, hurting the poor and failing to fix the very problems it warns us about. Lomborg explains ironically that “the rhetoric on climate change has become more extreme and less moored to the actual science” at the very time that “climate scientists have painstakingly increased knowledge about climate change, and we have more—and more reliable—data than ever before.”
Lomborg holds that while “global warming is real… it is not the end of the world.” “It is a manageable problem” he adds. He is increasingly dismayed that we live in a world “where almost half the population believes climate change will extinguish humanity” at the precise moment when “the science shows us that fears of a climate apocalypse are unfounded.” Demonstrating this is not difficult. Simply consider what we all need to live: air, water, abundant food, and protection from nature. Each of these are improving in dramatic ways precisely because of technology and growth. The scholars at Our World in Data and the Oxford Martin School at the University of Oxford demonstrate this.
The world’s air is getting cleaner overall, and markedly so.
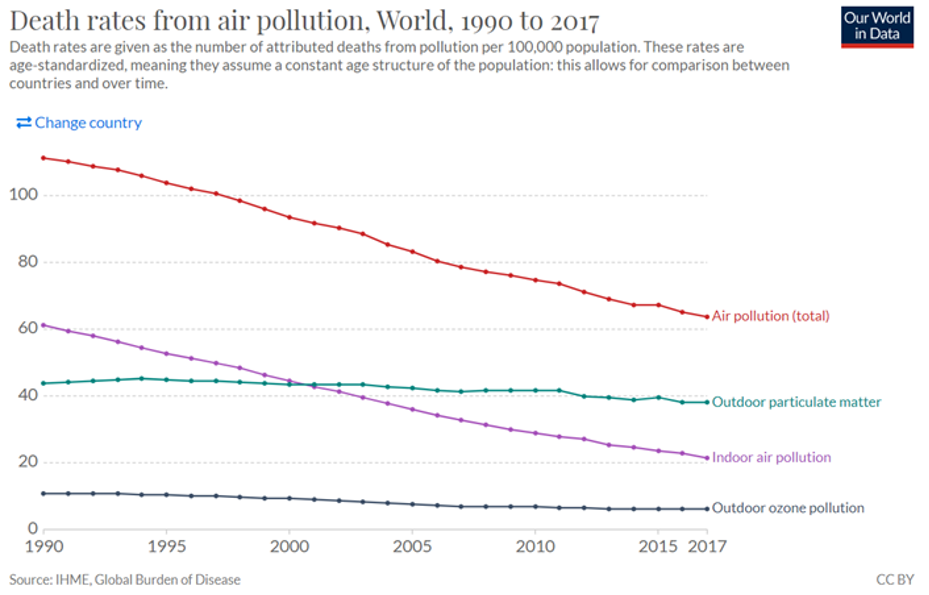
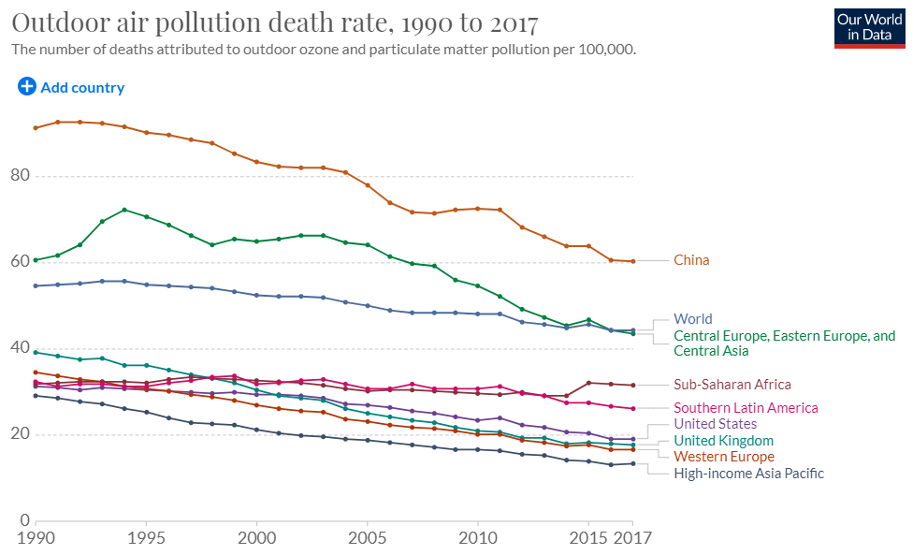
At the very time that population and industry have both grown dramatically across the globe, not only is the problem not getting worse, but human death rates from air pollution have declined by nearly half since just 1990. And it is not people driving less or living by fewer factories that’s saving lives. Counterintuitively, air pollution deaths are more than 100 times higher in non-industrial societies where cooking over wood or coal burning fires is a regular part of daily life. And as the world develops, such cooking declines. This means growth and technology are literally helping people breathe easier. And ozone pollution, or smog, has been declining rapidly throughout the world even in high-income, heavy manufacturing Asian Pacific regions.
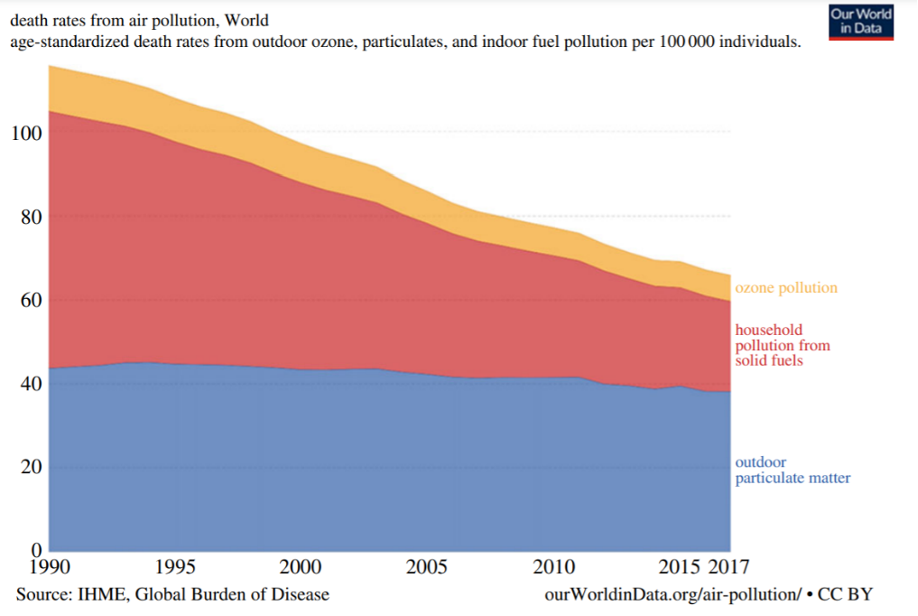
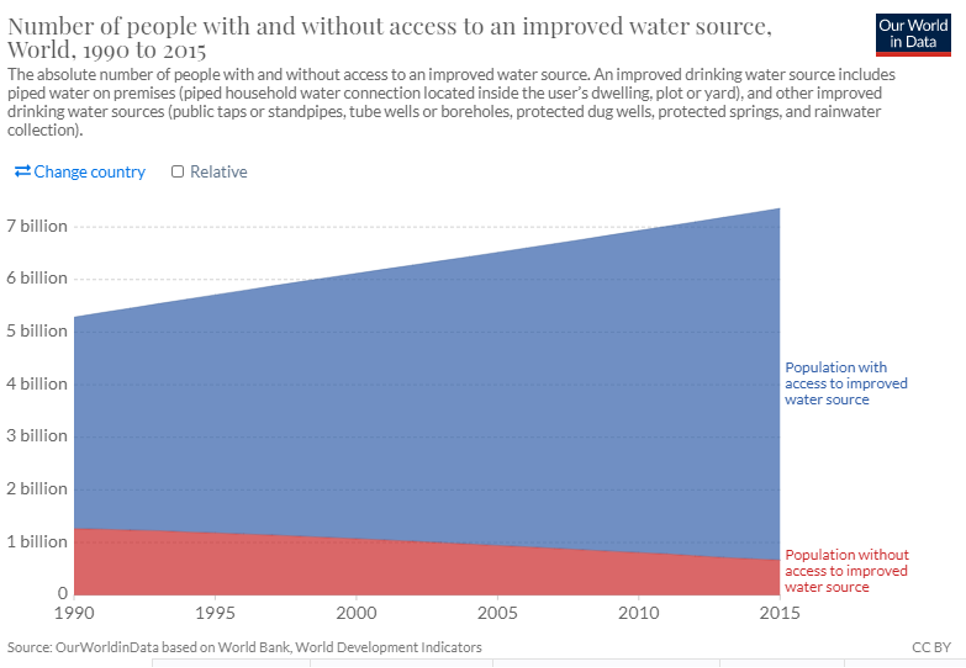
Water is humanity’s second most immediate life need. The number of people around the world with improved access to clean drinking water increased 68 percent from 1990 to 2015, even as the population itself has expanded. That is astounding. Roughly 290,000 people have gained access to improved drinking water every single day across the globe over the last 25 years and that number is only increasing of late.
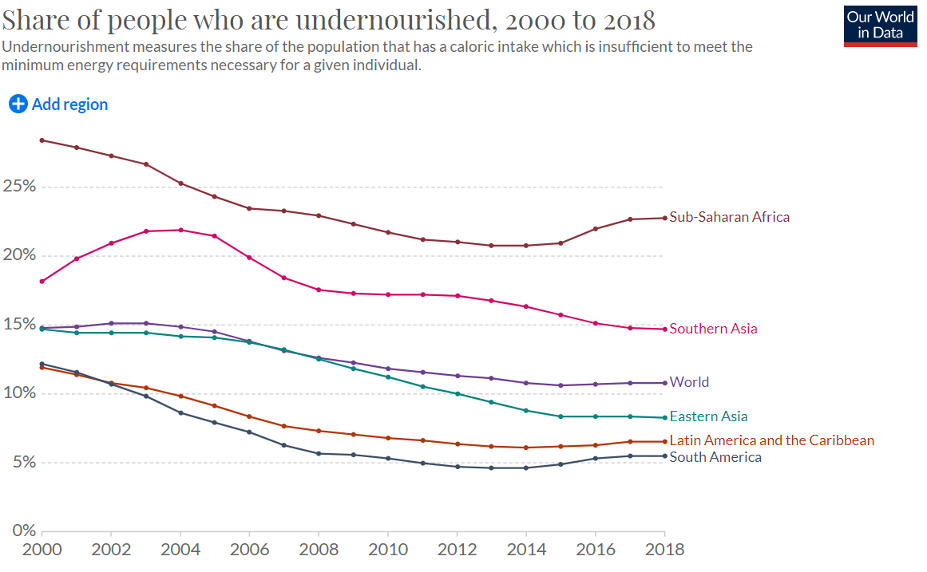
Food is our third greatest survival need. Contrary to grim Malthusian predictions, the United Nations explains that humanity now produces more than enough food to feed everyone on the planet. In fact, the Journal of Sustainable Agriculture revealed back in 2012 that “we already grow enough food for 10 billion people.” This is a 25 percent bounty over our current global population, a surplus which we will never need. And, as we will see in the next section, our world population is soon to top out at just 9.73 billion people and then start declining precipitously into the coming century. While we must do a better job politically at distributing that bounty, our food supply is not only more plentiful, but of better nutritional quality thanks to technology. It’s why malnutrition is declining dramatically across the world.
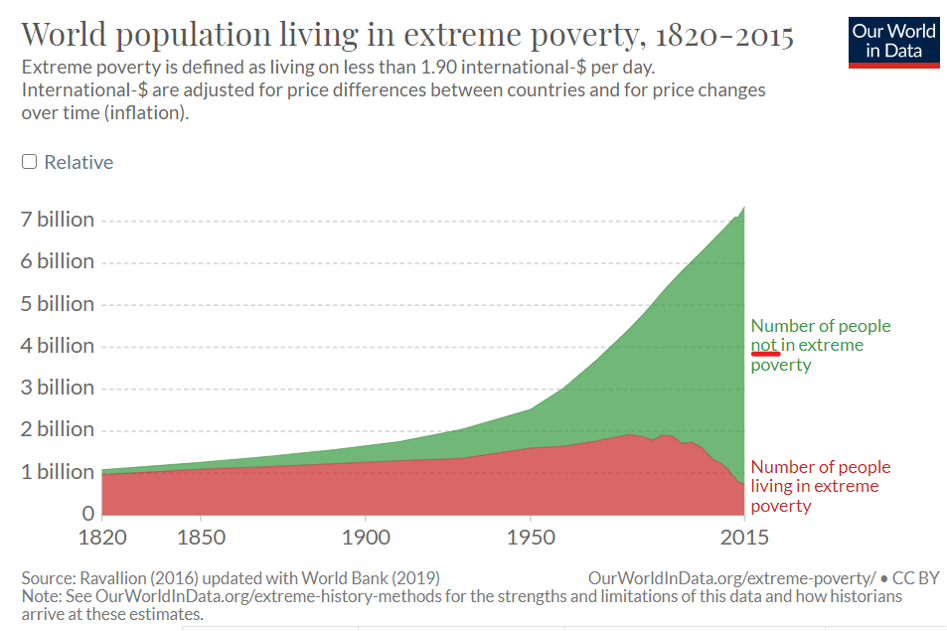
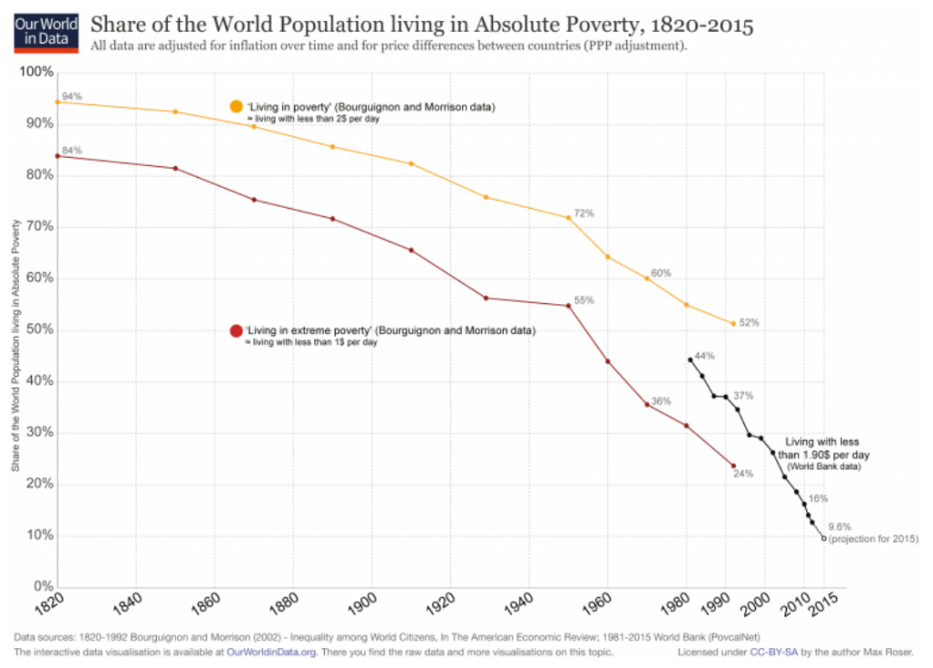
And the number of people around the world living in dramatic poverty is dropping, even as we grow in number—a direct refutation of ubiquitous Malthusian projections.
The Earth is actually doing better at providing what is needed to sustain human life as a consequence of human ingenuity of industry and technology. And what about the Earth itself? Let’s look at two important measures.
First, is it becoming more hospitable to human thriving, or less? A major 2019 study in the journal Global Environmental Change drawing from “one of the most complete natural disaster loss databases” reveals “a clear decreasing in both human and economic vulnerability” to “the seven most common climate-related hazards” by up to 80 to 90 percent over the last four decades. These hazards include all forms of flooding, drought, and deaths related to extreme wind, cold or heat. The trend lines are dramatic.
The scholars at Our World in Data add that this also holds for other natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcano activity, wildfire, and landslides. “This decline is even more impressive,” they explain, “when we consider the rate of population growth over this period” revealing a greater than 10-fold decline in nature-related human deaths worldwide over the last century.
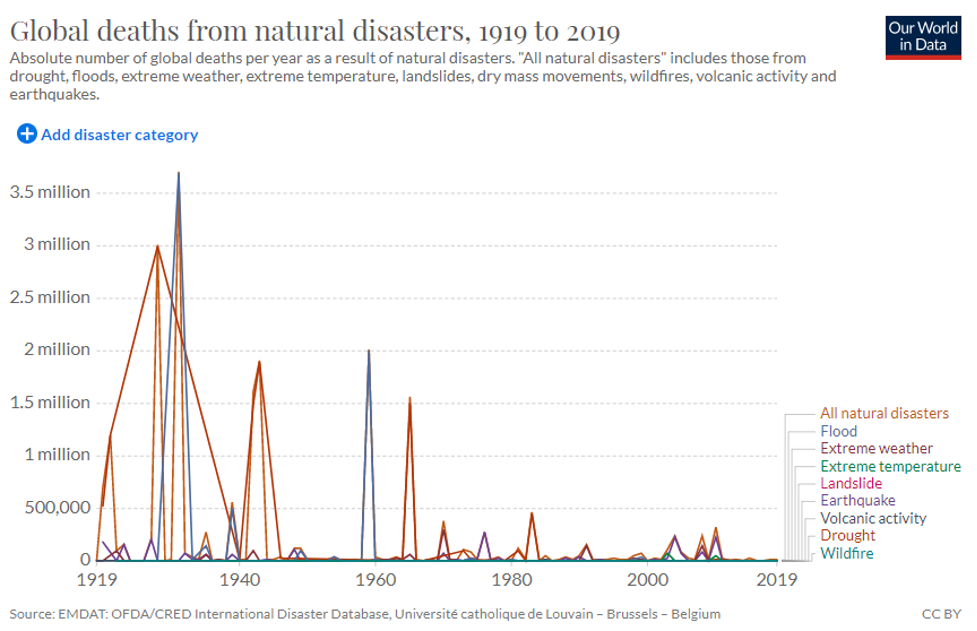
This means the Earth is becoming a much safer place for humans to live precisely because we are adapting to it better. That is precisely the opposite of catastrophe by most people’s honest math.
Second, is the Earth itself being more widely exploited or getting a break? The 2018 United Nations List of Protected Areas report (Table 1, p. 41) demonstrates that the total number of protected sites in the world has increased 2,489 percent since 1962 and the total protected terrestrial and aquatic area grew by 1,834 percent. The proportion of land used for all agriculture (crops and grazing) per person across the globe has plummeted dramatically over the last 100 years as technology allows us to grow more food than we can consume on less land per capita than ever before.
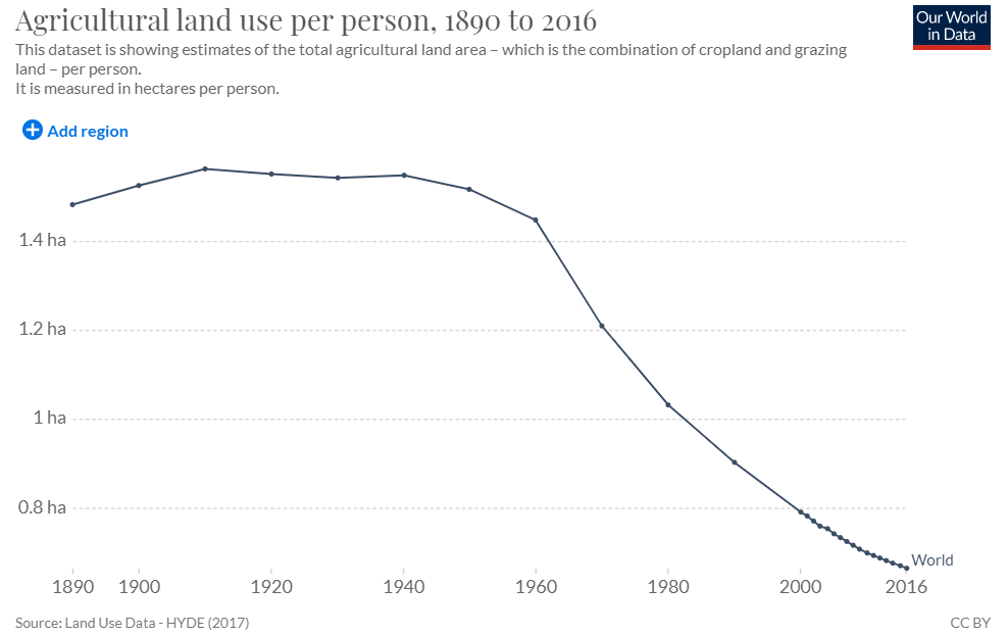
And this is true across all continents.
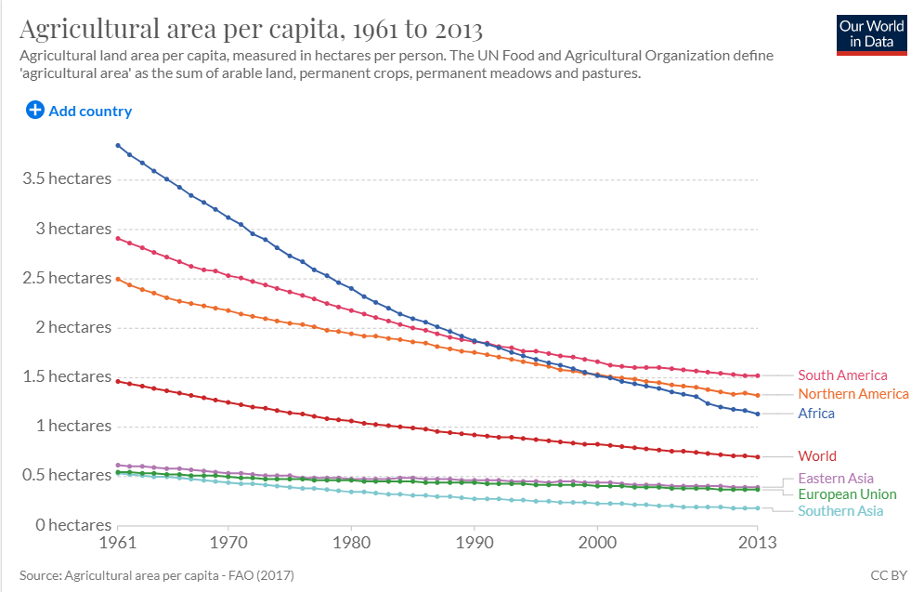
As stewards of the planet, we still have much work to do in improving the environment. But note the key word: improve. The empirical data persuasively indicate the most significant trend lines are moving in the right directions in profound ways for billions of people around the globe, and the reason is technology and human progress. These truths are the exact opposite of an eco-Armageddon.
What does the likeliest end of humanity look like?
So does this mean there are no concerns about humanity’s future? New research published this summer has many of the world’s leading scientists extremely concerned, much more so than when 2020 began. A major demographic study published in the Lancet in July provides a glimpse of humanity’s end if things continue as they are. This work was conducted by 24 leading demographers and funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. What concerns these scholars is certainly not too many people, as nearly everyone assumes, but a relatively near future of far too few.
Demographers have long been concerned about this. The “news” part here is how much more dire the Gates research is. Using a more sophisticated analysis than the United Nations and other leading global think tanks have employed to date reveals the world’s population shortfall will be markedly more dramatic, and sooner, than anyone anticipated. The BBC described it as a “jaw dropping global crash.” And none of these demographers see this as a good thing. Quite the opposite. No fewer than 23 leading nations—including Japan, Spain, South Korea, and Italy—will see their population cut in half by 2100. China’s will drop by a stunning 48 percent, knocking it out of contention as the world’s economic super-power. This precipitous decline will not be caused by disease, famine, or any kind of natural disaster. The missing population will simply never have been born. Their would-be parents are simply forgetting to have them.
Imagine any of these countries getting a military intelligence report that a foreign enemy was set to reduce their population by more than half over the next 60 years. But in this case, the dramatic act of war is self-inflicted by each country’s growing cohort of non-parents. Another 34 countries will see dramatic population declines by 25 to 50 percent by 2100. Beyond this, the projected fertility rates in 183 of 195 countries will not be high enough to maintain current populations by the century’s end. That is called negative population growth and once it starts, it probably won’t stop. These scholars predict that sub-Saharan and North Africa, as well as the Middle East, will be the only super regions fertile enough to maintain their populations without dramatic immigration policies.

To say the geopolitical and economic consequences of this fact will be profound is an understatement. The Gates research further darkens the already bleak picture painted last year by two Canadian researchers, Darrell Bricker and John Ibbitson, in their insightful and carefully documented book, Empty Planet: The Shock of Global Population Decline. They warn:
The great defining event of the twenty-first century—one of the great defining events in human history—will occur in three decades, give or take, when the global population starts to decline. Once that decline begins, it will never end. We do not face the challenge of a population bomb, but of a population bust—a relentless, generation-after-generation culling of the human herd. [emphasis added]
The Gates scholars agree with the Empty Planet scenario, marking 2064 as humanity’s demographic high-water mark at just 9.73 billion human souls, short of the long predicted 10 billion. Academic demographers are not given to hyperbole. The unsustainability at work here is extreme. The Gates team explains:
- The number of global citizens under five years of age will fall from 681 million in 2017 to 401 million in 2100, a 41 percent drop.
- The number of over 80-year-olds will soar from 141 million in 2017 to 866 million in 2100, a whopping 514 percent increase.
Imagine these are your company’s future customer projections. You don’t get to the future with numbers like this. Putting this in very stark, recent historical perspective, there were 25 worldwide births for every person turning 80 in 1950, a healthy demographic dividend. In 2017, that ratio shrank to 7:1. Not so healthy. These 24 Gates demographers explain, “in 2100 we forecasted one birth for every person turning 80 years old.” (See it for yourself at p.1297.)
This is what the end of humanity looks like. Professor Christopher Murray, director of the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington’s School of Medicine and head of the Gates study, told the BBC, “I find people laugh it off… they can’t imagine it could be true, they think women will just decide to have more kids. If you can’t [find a solution] then eventually the species disappears.” And the solutions that developed countries have tried of late are not working.
The twilight of economic and technological growth
Few scholars have appreciated the full consequences of this implosion like Professor Charles Jones of Stanford University’s King Center on Global Development. In October, he published a persuasive paper entitled ‘The End of Economic Growth? Unintended Consequences of a Declining Population,’ in which he asked what happens to global economic and technological growth, not just when population growth slows or goes to zero, but actually turns negative? Elaborating upon Bricker and Ibbitson’s work, he contends that we must consider what he calls “an Empty Planet result” where “knowledge and living standards stagnate for a population that gradually vanishes.”
Like Shellenberger, Jones is “pro-people” for empirical reasons. He explained to me that contrary to nearly all demographic predictions, “we simultaneously have many more people and much higher living standards” precisely because “people are a crucial input into the production of the new ideas responsible for economic growth.” Jones calls our attention to the groundbreaking work of his mentor, economist Paul Romer, on Endogenous Growth Theory, which explains why more people are not only a good thing but essential to improvements in human thriving and a better world documented above.
Their concern is far more nuanced than fewer babies not becoming the needed taxpayers to support tomorrow’s mushrooming non-working elderly. Endogenous Growth Theory is more subtle and elegant as it actually explains our current developing world. In a 2019 paper in the Scandinavian Journal of Economics, Jones calls Endogenous Growth Theory “truly beautiful,” a superlative seldom employed by nerdy economist types. It earned Romer the 2018 Nobel Prize in Economics.
Thomas Malthus saw new people as zero-sum consumers of our precious limited resources. Thus, fewer are better. Romer’s Endogenous Growth Theory demonstrates precisely why Malthus was so spectacularly wrong. He failed to appreciate that humanity’s power as innovators is positively and exponentially greater than our collective drag as consumers. Romer recognized why, rather than devastating scarcity, which breeds fear and drives the need to control, a rapidly growing human population has actually produced unimagined abundance. Human ingenuity and innovation are far richer blessings to the world than our appetites are a curse. The latter drives the former.
And this is not just happy talk. The data bears it out. More people are the answer to a better world for everyone. This is why our global political moment is so critical. Policies that favor difference and competing ideas are where growth happens. That is precisely what good science and democracy require. Death happens when competing ideas are shut down in favor of strictly enforced homogeneity. Endogeny requires the dynamic competition of heterodox ideas so that they can be aired, challenged, and refined by others. Current “progressive thought” is really a new fundamentalism that is contrary to growth. It is fear-based and leads to death. This is precisely what we are seeing today.
The magic of what Romer and Jones describe is found in the codification of human knowledge and the non-rivalry of ideas. Natural resources are what economists call “rival.” You and I cannot eat the same potato or drink the same glass of water simultaneously. We must either compete for it or produce twice as much. But the idea of how to find and store more potatoes or water is non-rival. It can be written down and shared all around the world by people at the same time without diminishing its full power. So, as Jones explains, “because knowledge is non-rival, growth in the aggregate stock of knowledge at the rate of population growth will cause income per person to grow.” [p. 878, emphasis in original]
Oral rehydration theory is one of Romer’s favorite examples of the power of codified ideas. Dehydration from diarrhea has long been the primary driver of child mortality—deadlier than AIDS, malaria, and measles combined. As Jones explains, some medical workers discovered that “dissolving a few inexpensive minerals, salts, and a little sugar in water in just the right proportions produces a solution” that prevents death from dehydration. That relatively simple recipe could be written down, shared, and used by billions at the same time. It has since saved untold lives. Objects are rival. Ideas are non-rival and thus, exponentially powerful. And humans are the globe’s only inhabitants that produce ideas. And when growing groups of people cooperate around and share these ideas, stunning things happen. This is Endogenous Growth Theory and it explains the wonder of the modern world in which we have more wealth and food at a time when we have the most people. Malthus and his disciples said the opposite would happen.
Romer entitled his 2018 Nobel acceptance talk in Stockholm “On the Possibility of Progress,” as an obvious challenge to Malthus, and at an efficient 30 minutes, his lecture is worth watching. He spoke of how his work—and that of Yale’s William Nordhaus, his co-recipient—demonstrates “the benefit of other people.” Our scientific, industrial, and tech revolutions, and their dramatic improvements to human flourishing, were, he explains, “driven by a process of more discoveries, leading to the production of more food, which led to more people, who in turn developed more and more discoveries” which have improved the lives of billions. As Romer explains, “This is not just exponential growth. This is exponential growth in the rate of exponential growth…”
He went on to explain that this “combinatorial explosion” of more people cooperating around ever-growing, world-changing, life-improving ideas makes it “immediately obvious that the discovery of new ideas from an almost infinite set of possibilities could offset the scarce resources implied by the Malthusian analysis.” And it obviously has. If the eco-doomsayers could choose to live at any time in human history, they would undoubtably choose today if their dream is physical safety and a long, prosperous, and contemplative life with an abundance of essential resources and a substantially improving eco-system.
As Romer explained to his Nobel audience on that lovely winter evening in Stockholm, Endogenous Growth Theory is the beautiful explanation of why, “on balance, it is better to have more people” rather than fewer. Limiting our population is not a progressive idea. The most sophisticated, cross-disciplinary science emerging from academia appears to tell us that the ancient Mosaic wisdom of the Judeo/Christian tradition, to “be fruitful and multiply and fill the earth” is exactly the correct progressive prescription for the continuation of human well-being. And failing to do this is what the end of the world actually looks like.